BOOK: AOD Foundations
This book will provide an overview of some of the background and considerations in designing and facilitating an AOD. It's full of resources and examples to inspire your thinking.
6. Writing a Prompt
6.1. Blooming Questions
What is Bloom's Taxonomy
The Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, known as Bloom's Taxonomy (Bloom, Engelhart, Furst, & Krathwohl, 1956) is one of the most recognized learning theories in the field of education. Educators often use Bloom's Taxonomy to create learning outcomes, or write questions, that target not only subject matter but also the depth of learning they want learners to achieve (Anderson & Krathwohl, 2001).This taxonomy encompasses six levels, each representing a stage of understanding that builds upon the previous one. At the base is Knowledge, which involves the recall of facts and basic concepts. Comprehension follows, requiring learners to understand and interpret information. The third level, Application, involves using knowledge in new situations. Analysis comes next, where learners dissect information to understand its structure. The fifth level, Synthesis (revised to Creating in later versions), entails compiling information in novel ways. Finally, Evaluation, the highest level, involves making judgments based on criteria and standards. In recent years, the order of synthesis and evaluation has been flipped from the picture shown below.
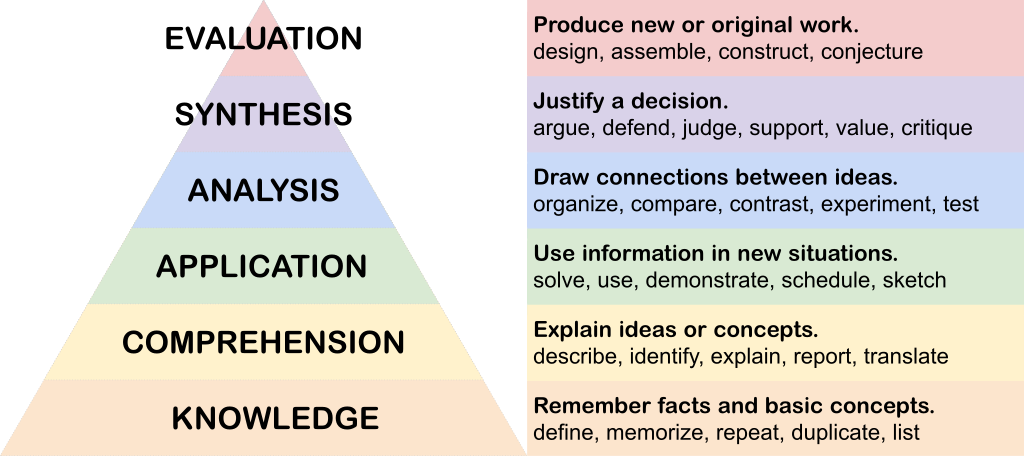
This hierarchical structure emphasizes that mastering higher levels requires proficiency in the preceding levels, guiding educators in designing activities that foster deeper learning and critical thinking skills.
How to Use Bloom to Write a Prompt
Bloom's verbs are action words associated with each level of Bloom's Taxonomy. By employing these verbs in a prompt, educators can design discussions that target a specific cognitive level.
To use a Bloom's Taxonomy verb in an AOD prompt, start by identifying the cognitive level that your activity should target. What's your learning objective with this discussion? For instance, if the goal is to enhance critical thinking, you might choose "analyze."
Then, select a Bloom verb that corresponds to the desired cognitive level of understanding from the table below. Incorporate this verb into your prompt in a way that clearly directs participants to engage at the specified level of cognition. For example, if targeting "analyze," your prompt could ask participants to dissect a given argument and identify its underlying assumptions.
Knowledge |
Comprehension |
Application |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Analysis |
Synthesis |
Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
References
Anderson, L., & Krathwohl, D. A. (2001). Taxonomy for learning, teaching and assessing: A revision of Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives. New York: Longman.
Attributions
Centre for Teaching Excellence (n.a.). Bloom's Taxonomy. University of Waterloo. https://uwaterloo.ca/centre-for-teaching-excellence/catalogs/tip-sheets/blooms-taxonomyCentre for Teaching Excellence (n.a.). Asking Questions: Six Types. University of Waterloo. https://uwaterloo.ca/centre-for-teaching-excellence/catalogs/tip-sheets/asking-questions-six-types
Centre for Teaching Excellence (n.a.). Bloom's Taxonomy Learning Activities and Assessments. University of Waterloo. https://uwaterloo.ca/centre-for-teaching-excellence/catalogs/tip-sheets/blooms-taxonomy-learning-activities-and-assessments
Image of Bloom's Taxonomy
Douglas Perkins, CC BY 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons